The system of continuous monitoring of blood glucose to control the diabetes
At Medpark, the patients can benefit from the newest method of investigation for persons suffering from diabetes – the continuous monitoring of blood glucose (sugar level in blood).
The innovational technology allows an extremely efficient evaluation of glycemic control, impossible to perform through other existing means. This method is done by implanting (introducing) a special sensor in the subcutaneous tissue (under the skin). The glycemic sensor is individual and it can be worn during 5-7 days, the glucose concentration being measured every 10 seconds and recorded every 5 minutes, thus, providing up to 288 measurements per day.
A small recorder, endowed with sensors, collects and stores the obtained data. After 5-7 days, the sensor is removed and the registered data is downloaded into a computer program, which analyzes de data and executes daily reports regarding the glycemic profile, presented as a graphic. Thus, the information regarding the glucose level in the blood is collected every 5 minutes during 5-7 days, which makes it possible to obtain a complete and detailed image of glycemic variations of the person under examination. The obtained data facilitates the adjustments of therapeutic schemes, aiming at optimizing the glycemic control.
Compared to the glycemic monitoring with the help of a glucometer, the continuous monitoring provides a much wider information regarding the daily glucose level. The conventional monitoring (with the glucometer) is discontinuous and, as a consequence, quite often, the hypo- and hyperglycemic episodes are overlooked and are not conveyed even with the help of frequent tests. The difference between the information obtained with the help of continuous monitoring and the one provided by the glucometer is like comparing a photograph with a video tape. The continuous monitoring of glucose offers a much larger perspective upon the glycemic levels during 24 hours, allows to identify some frames of daily evolution of the glycemic data and to take the necessary measurements in order to prevent the apparition of hypo- and hyperglycemia.
In term of diabetes control, this means that you can have more information than ever before and see what happens to the glucose level: during the night, during physical activities, after certain meals or even during a working day compared to a day off. The collected information allows the doctor to personalize the treatment according to individual reaction to physical exercise, carbohydrates intake and antidiabetic medication.
The continuous monitoring of glucose enables you to react in a timely manner, reducing the risk of any long-term complications.
Who can benefit from continuous monitoring of glucose?
Patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, who:
- Do not obtain the aimed value of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) – an index reflecting the state of diabetes compensation and correlates with the development of diabetes complications;
- Present recurrent (repeated), frequent hypoglycemia;
- Present nightly hypoglycemia and/or possible silent (without any symptoms) hypoglycemia;
- Do not know how to read the glycemic profile results, as well as how to adjust the insulin dose;
- Are not motivated to auto-monitor the glucose with a glucometer;
- Patients who want to evaluate the effects of different foods or physical activities upon the glucose levels in blood.
What is the continuous monitoring of glucose used for?
- To adjust a therapeutic scheme;
- To diagnose and to prevent nightly hypoglycemic episodes;
- To diagnose and to prevent postprandial (after meals) hypo-/hyperglycemia;
- To adapt food habits and physical exercise;
- To educate/reeducate the patient, to increase compliance to the treatment.
How is the continuous monitoring of glucose performed?
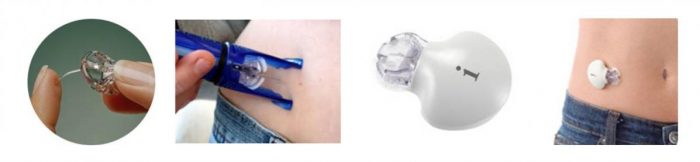
There are 3 simple steps for research with the help of the iPro Continuous Monitoring System of Glucose:
I. The first visit to the doctor (20-30 min):
- The medical worker introduces the sensor
- Instruction to the patient while the sensor is being hydrated
- The medical worker connects the recorder to the sensor
II. The patient is at home
- Continues to perform his/her daily activity:
- Determines glucose level with the help of an electronic glucometer, at least 4 times a day
- Writes down the performed activities, the consumed foods, the taken medication
- The sensor can be kept for 5-7 days, where circa 280 glycemic values will be collected and stored daily. Having the sensor does not impede in any way the normal daily activity.
III. The 2nd visit to the doctor:
- The medical worker removes the sensor
- The information stored in the recorder is downloaded into a computer
- The medical worker prepares a report
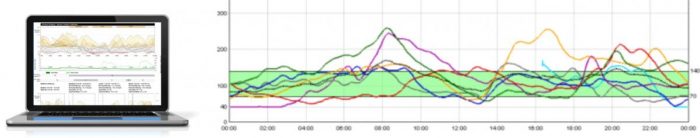
Analyzing the obtained curves, it is possible to deduct the elements, which influence glycaemia, to think out therapeutic strategies and to decide upon the treatment, in order to perform and maintain an optimal glycemic control.
Dr. Elena Mornealo, endocrinologist-nutritionist, Medpark

